The Eight Parts of Speech in English (PDF)
In this article, we will provide a clear overview of the eight parts of speech in English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
What are the eight parts of speech?
Think of parts of speech as roles within a sentence. Just as people can have different job titles-such as soldier, teacher, or baker-words can serve different purposes depending on their function.
- Noun – dog, city, love
- Pronoun – I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Verb – run, be, have, do, take
- Adjective – blue, happy, tall, friendly
- Adverb – quickly, well, very, here
- Preposition – in, on, at, with, by
- Conjunction – and, but, or, yet, so
- Interjection – oh, wow, ouch, hurray
Down below, you will find downloadable worksheets, grammar poster PDFs with examples of each part of speech, and more. You can use them in your classroom activities.
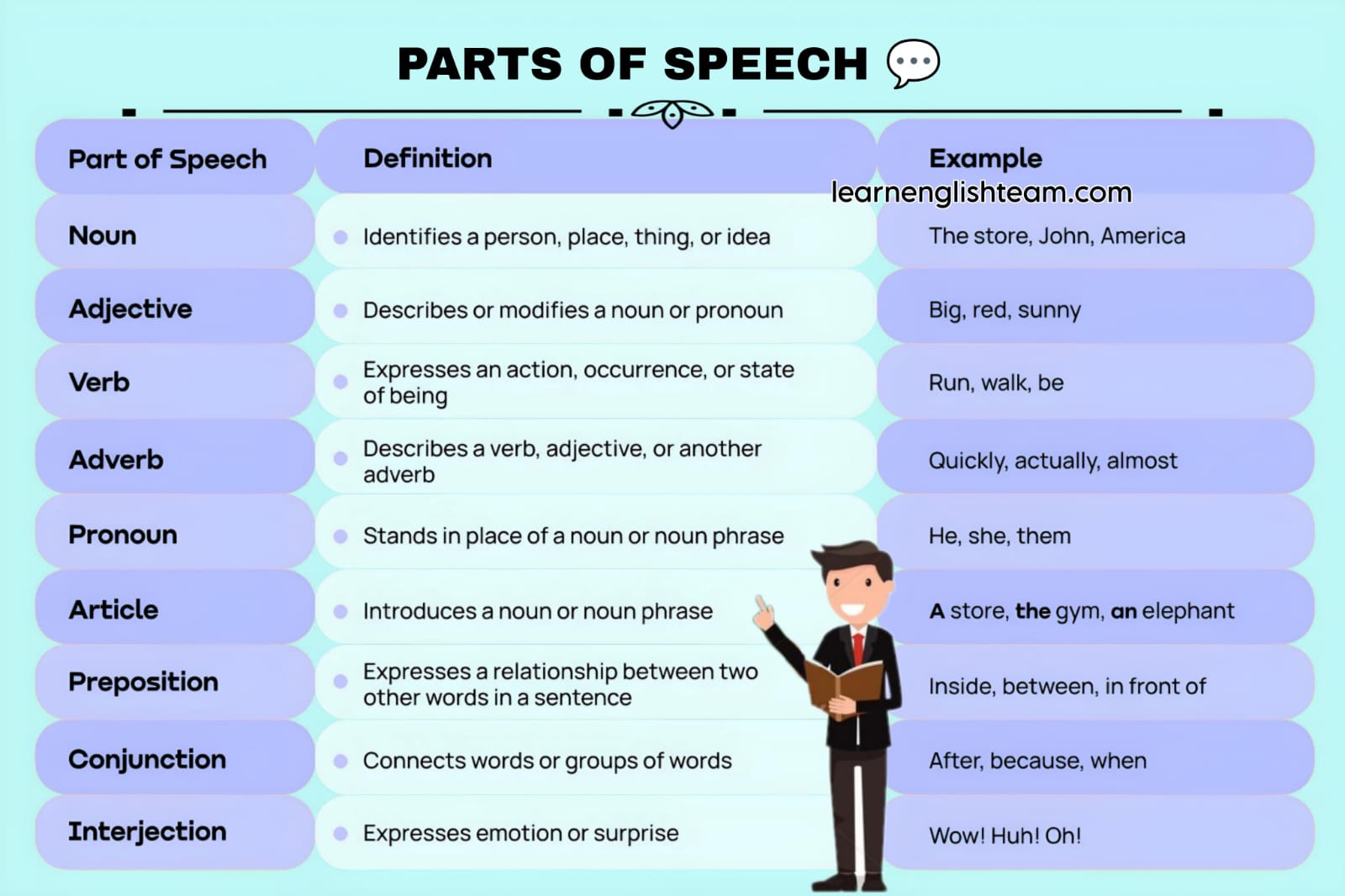
Parts of Speech Grammar Table
Parts of Speech PDF
Here you can download parts of speech poster, worksheet PDFs with examples.
Parts of Speech in English PDF - download
Simple Parts of Speech Worksheet - download
Parts of Speech Grammar Poster - download
The 8 Parts of Speech
1. NOUN
noun is a word (other than a pronoun) used to identify any of a class of people, animals, places, things, ideas.
Nouns are separated into common nouns and proper nouns.
What is a common noun?
Common nouns are used for people, animals, places, or things.
Example: granny, mother, river, mountain, hotel, taxi, fox, camel.
He is an artist.
Tom hates bananas.
I love my mother.
Her father is a doctor.
What is a proper noun?
Proper nouns are names for particular people, places or things. They always begin with a capital letter.
Example: Ali Baba, Harry Potter, Beethoven, Turkish, British, Malay, Hong Kong, India, The United Kingdom,the Pacific Ocean, the Eiffel Tower, Father’s Day, Ramadan, Halloween.
☛The days of the week and months of the year are also proper nouns.
December is the last month of the year.
Sunday is the last day of the week.
What is singular and plural noun?
When you are talking about one person, animal, place, or thing, use a singular noun.
Example: a ship, a teacher, a river, an apple, an umbrella.
When you are talking about two or more people, animals, places, or things, use plural nouns. Most nouns are made plural by adding -s at the end.
Example: ships, teachers, rivers, apples, umbrellas
Some exceptions:
bus-buses. glass-glasses. watch-watches. brush-brushes.
butterfly-butterflies. baby-babies. lady-ladies. story-stories.
☛Nouns show possession by adding ‘s.
☛Tom’s car.
☛Car’s key.
What is concrete and abstract noun?
Concrete nouns are things you can experience (see, hear, smell, touch, or taste) with your senses. Here are some examples: tree, music, flowers, and chocolate.
Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived through the senses. Examples include love, honesty, joy, and freedom.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of nouns in English:
| Noun Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Common Nouns | book, table, city, person |
| Proper Nouns | Muhammad, London, Mary, Toyota, Amazon |
| Concrete Nouns | tree, music, flowers, chocolate |
| Abstract Nouns | love, honesty, joy, freedom |
| Collective Nouns | team, family, herd, flock |
| Countable Nouns | cat, dog, chair, student |
| Uncountable Nouns | water, air, happiness, information |
| Compound Nouns | toothbrush, software, basketball |
| Possessive Nouns | John’s, cat’s, company’s, children’s |
| Plural Nouns | books, tables, cities, people |
| Gerunds | swimming, reading, writing |
Check Also:
Common and Proper Nouns Explained (Exercise and Examples)
Masculine and Feminine Nouns in English
100 Most Common English Nouns A-Z List (PDF)
2. PRONOUN
A pronoun is a word that can replace a noun in a sentence.
Personal Pronouns: The words I, you, he, she, it, we and they are called personal pronouns.
He is a nice guy.
You are welcome.
Possessive Pronouns: The words mine, yours, hers, his, its, theirs, ours, yours, theirs are called possessive pronouns.
This car is mine.
Time is yours.
Reflexive Pronouns: The words myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves and themselves are called reflexive pronouns.
Maryam has hurt herself.
Don’t cut yourself.
Demonstrative Pronouns: The words this, these, that and those are called demonstrative pronouns.
This is my car.
These are my flowers.
Interrogative Pronouns: The words who, whom, whose, what and which are called interrogative pronouns. We ask questions by using these pronouns.
Who is she talking to?
Which do you prefer?
Here’s a table with examples of different types of pronouns in English:
| Pronoun Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Personal Pronouns | I, you, he, she, it, we, they |
| Possessive Pronouns | mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs |
| Reflexive Pronouns | myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves |
| Demonstrative Pronouns | this, that, these, those |
| Interrogative Pronouns | who, whom, whose, which, what |
| Relative Pronouns | who, whom, whose, which, that |
| Indefinite Pronouns | all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, none, no one, nothing, one, other, several, some, somebody, someone, something, both, few, many, several |
| Reciprocal Pronouns | each other, one another |
Check Also:
Personal & Possessive Pronouns for English Learners
Nobody, No one, None Difference & Examples
Difference Between Who and Whom
3. VERB
A word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence, and forming the main part of the predicate of a sentence, such as hear, become, happen, run, eat.
Most verbs are action words. Verbs shows you what people, animals or things are doing.
Verbs can show actions or they can show states or situations.Those are the two types of verbs in English.
☛I am eating. – verb (eat) shows an action.
☛I am a student. verb (to be) shows a state.
☛Verbs also change and take different forms to show tenses.
I drink a lot of water ☛ I drank a lot of water yesterday.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of verbs in English:
| Verb Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Action Verbs | run, jump, eat, write, sing |
| Linking Verbs | am, is, are, was, were, appear, seem, become, feel, look, sound, taste, smell |
| Helping Verbs | can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must, have, has, had, do, does, did |
| Modal Verbs | can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must |
| Transitive Verbs | carry, build, eat, write, teach |
| Intransitive Verbs | arrive, exist, sleep, laugh |
| Regular Verbs | walk, talk, play, watch |
| Irregular Verbs | go, have, be, see, swim, eat |
| Phrasal Verbs | look up, give in, turn off |
| Infinitive Verbs | to run, to eat, to study |
| Gerunds | running, eating, studying |
Check Also:
500+ English Verbs List (V1 V2 V3 Verb Forms) + PDF
Most Common English Verbs & Synonyms List (PDF)
All forms of the verb TO BE and Its Usage
4. ADJECTIVE
An adjective is a describing word. Adjective describes a noun or a pronoun.
The red carpet.
Deep thoughts.
A busy street.
She is beautiful today.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adjectives in English:
| Adjective Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Descriptive Adjectives | tall, blue, happy, delicious |
| Quantitative Adjectives | many, few, some, several, all |
| Demonstrative Adjectives | this, that, these, those |
| Possessive Adjectives | my, your, his, her, its, our, their |
| Interrogative Adjectives | which, what, whose |
| Indefinite Adjectives | some, any, many, few, several, all |
| Comparative Adjectives | taller, bluer, happier, more delicious |
| Superlative Adjectives | tallest, bluest, happiest, most delicious |
Check Also:
List of Opposite Adjectives in English (PDF)
Positive Adjectives to Describe a Person (PDF)
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives List + PDF
5. ADVERB
A word that describes a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or a sentence. It tells you about an action, or the way something is done.
☛A lot of adverbs end in -ly.
We are happily married.
Tom calls me regularly.
Suddenly, she knows. It’s love!
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adverbs in English:
| Adverb Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Adverbs of Manner | quickly, slowly, happily, carefully |
| Adverbs of Place | here, there, everywhere, nowhere |
| Adverbs of Time | now, later, yesterday, soon |
| Adverbs of Frequency | always, often, sometimes, rarely, never |
| Adverbs of Degree | very, too, quite, almost, absolutely |
| Interrogative Adverbs | how, when, where, why |
| Relative Adverbs | when, where, why |
| Conjunctive Adverbs | however, therefore, meanwhile |


Check Also:
Types of Adverbs in English & Meaning and Examples (PDF)
Common Suffixes in English (With Examples) & PDF
6. PREPOSITION
A preposition is a word that connects one thing with another, showing how they are related.
Prepositions tell us about time, position or place.
Some examples of prepositions are words like ‘in,’ ‘at,’ ‘on,’ ‘of,’ ‘to,’ ‘from.’
She is in love.
Book was on the table.
I am from France.
He is calling to you.
Where are you at?
Here’s a table categorizing types of prepositions with examples:
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Prepositions of Place | above, across, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, in, into, near, on, over, through, under, with |
| Prepositions of Time | after, before, during, for, from, in, on, over, through, to, until, with |
| Prepositions of Direction | across, along, around, behind, beyond, into, through, to |
| Prepositions of Agent/Instrument | by, with |
| Prepositions of Manner | like, unlike, after, as |
| Prepositions of Purpose | for, to, in order to |
| Prepositions of Source/Origin | from, out of |
Check Also:
Complete List of English Prepositions A-Z (Free PDF)
Commonly Used Prepositions Lists in English
Common Collocations in English With Prepositions (PDF)
Prepositions of Location At, In & On (PDF)
7. CONJUNCTION
A conjunction is a linking word that used to connect clauses or sentences. For example and, or, but, as, if.
Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses together.
a teacher and students.
a male or female?
☛Words such as before, after, as, when, while, until, since, are conjunctions of time.
Maryam could play guitar before she was four.
She always brush her teeth after eating her meal.
There are four categories of conjunctions:
| Type | Conjunctions |
|---|---|
| Coordinating Conjunctions | for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so |
| Correlative Conjunctions | both/and, either/or, neither/nor, not only/but, whether/or |
| Subordinating Conjunctions | after, although, as, as if, as long as, as much as, as soon as, as though, because, before, by the time, even if, even though, if, in order that, in case, in the event that, now that, once, only, only if, provided that, since, so, supposing, that, than, though, till, unless, until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, whether or not, while |
| Conjunctive Adverbs | however, therefore |
8.INTERJECTION
An interjection is a word that expresses an emotion, sudden, strong feeling such as surprise, pain, or pleasure.
☛It is often followed by an exclamation point.
| Expression | Example |
|---|---|
| Cheers! | Cheers to a great day! |
| Ouch! | Ouch! That hurt. |
| Oh my God! | Oh my God! Is that true? |
| Oh dear! | Oh dear! What happened? |
| Good luck! | Good luck on your exam! |
| Help! | Help! I need assistance. |
| Gosh! | Gosh! That’s amazing. |
| Hey! | Hey! How are you? |
| Look out! | Look out! There’s a car coming! |
Check Also:
Interjections in English Grammar & List Examples
1000+ Common Daily English Phrases for Beginners (PDF)





Best examples for the students
Pratik dhamane
Useful lecture for whom studying English language from beginning. we hope you to upload more grammar lecture in pdf form
Sure! Don’t forget to subscribe our new lessons. 🙂
Very nice, thanks for the PDF.
Thanks for free PDF file.
I’m really enjoy Learning English.l find to the best to me
James