Common Errors in English and How to Correct Them (PDF)
Mastering English grammar is crucial for clear and effective communication. Many learners make similar errors, which can impact the clarity of their writing and speaking. This article highlights common grammar mistakes and provides practical tips to correct them, helping you improve your English skills.
Common Mistakes in English
1. Present and Past Tense Errors
Understanding and correctly using tenses is fundamental in English. Here’s a quick overview of the four present tense forms:
- Present Simple: I work
- Present Continuous: I am working
- Present Perfect: I have worked
- Present Perfect Continuous: I have been working
Past Tense Usage: Use the past tense to describe events or situations that have concluded. For instance: “When I was a child, I lived in the countryside.”
Common past tense verbs include: was, were, and went.
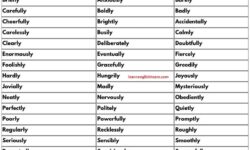
2. Avoiding Adverb Overuse
Adverbs can enhance descriptions, but overusing them can clutter your writing. Instead of relying heavily on adverbs to describe actions, focus on showing rather than telling.
Overused Adverb Example: “The curtain opened quickly, and Ben walked aggressively towards Emma.”
Improved Example: “The curtain opened. Ben stormed over to Emma.”
3. Confusing “Your” and “You’re”
These homophones often cause confusion. Remember:
- “Your” indicates possession. Example: “Your book.”
- “You’re” is short for “you are.” Example: “You’re amazing.”
Incorrect Usage: “Your going to love this.”
Correct Usage: “You’re going to love this.”
4. Apostrophe Misplacement
Apostrophes show possession or indicate contractions. Common errors include:
- Singular Possession: “The girl’s book.”
- Plural Possession: “The girls’ room.”
- Contractions: “Can’t” for “cannot.”
Incorrect: “The girls book is on the table.”
Correct: “The girl’s book is on the table.”
5. Differentiating “There,” “Their,” and “They’re”
These homophones are often confused:
- “There” refers to a place. Example: “Over there.”
- “Their” shows possession. Example: “Their car.”
- “They’re” is short for “they are.” Example: “They’re excited.”
Incorrect: “We should go their now.”
Correct: “We should go there now.”
6. Confusing Similar Words
Words that sound or look alike can be tricky. Common pairs include:
- “Two” vs. “Too” vs. “To”
- “Here” vs. “Hear”
- “Weather” vs. “Whether”
Incorrect: “I need to much time.”
Correct: “I need too much time.”
7. Incomplete Comparisons
When making comparisons, ensure they are complete:
Incomplete: “It was hotter today.”
Complete: “It was hotter today than yesterday.”
8. Adjective vs. Adverb Confusion
Adjectives describe nouns, while adverbs modify verbs. Misusing them can make your writing less precise.
Incorrect: “She sings beautiful.”
Correct: “She sings beautifully.”
9. Misplaced Modifiers
Modifiers should be placed close to the word they describe to avoid confusion.
Misplaced Modifier: “He almost walked for the entire day.”
Correct Modifier: “He walked for almost the entire day.”
10. Pronoun Disagreement
Ensure pronouns agree in number with their antecedents.
Incorrect: “Every student must hand in their paper.”
Correct: “Every student must hand in his or her paper.”
Examples of Common English Errors
- Wrong: I am married with a doctor
Right: I am married to a doctor - Wrong: We were boring in the school
Right: We were bored in school - Wrong: Every student like holidays
Right: Every student likes holidays - Wrong: I enjoyed from the concert
Right: I enjoyed the concert - Wrong: I am agree with you
Right: I agree with you - Wrong: Where I can find a girlfriend?
Right: Where can I find a girlfriend? - Wrong: I live in UK
Right: I live in the UK - Wrong: He doesn’t listen me
Right: He doesn’t listen to me - Wrong: Weather is more hot now
Right: The weather is hotter now - Wrong: Thank
Right: Thanks - Wrong: She doesn’t know how to make cake
Right: She doesn’t know how to make a cake - Wrong: I have visited to Paris last year
Right: I visited Paris last year - Wrong: He can plays the guitar very well
Right: He can play the guitar very well - Wrong: I will call you when I will arrive
Right: I will call you when I arrive - Wrong: The book was boring to read
Right: The book was boring to read