Learn English Verb Tenses in 10 Minutes + PDF
Understanding and learning English verb tenses can feel exhausting, but with the right approach, you can learn them quickly and effectively. This guide breaks down the tenses into simple, easy-to-understand concepts and provides practical tips to help you grasp each one.
The most basic English sentence requires a subject and a verb. The subject tells us who or what the sentence is about, and the verb tells us what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject. For example:
- Subject + Verb
- I + run.
- She + sings.
What Are Verb Tenses?
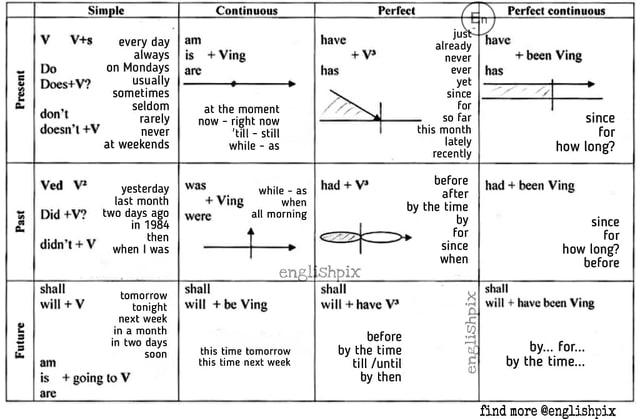
Verb tenses in English show the time of an action or state of being. There are 12 basic tenses, each with its own structure and usage.
Present Tenses
Present Simple

Structure: Subject + base verb (he/she/it + base verb + s/es)
Talk, walk, play, for (he,she,it) talks, walks, plays.
Use: Describes habits, general truths, and routines.
Examples:
- I play tennis every Sunday.
- You read books often.
- He walks to school.
- She likes ice cream.
- It rains a lot here.
- We enjoy movies.
- They travel frequently.
Present Continuous

Structure: Subject + am/is/are + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions happening right now or around the present time.
Examples:
- I am reading a book.
- You are eating lunch.
- He is playing football.
- She is watching TV.
- It is raining now.
- We are studying English.
- They are cooking dinner.
Present Perfect

Structure: Subject + have/has + past participle
Use: Describes actions that happened at an unspecified time before now.
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- You have visited Paris.
- He has bought a new car.
- She has seen that movie.
- It has stopped raining.
- We have traveled to Japan.
- They have started a new job.
Present Perfect Continuous

Structure: Subject + have/has + been + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
Examples:
- I have been studying for two hours.
- You have been working hard.
- He has been playing the guitar.
- She has been cooking dinner.
- It has been raining all day.
- We have been learning English.
- They have been building a house.
Past Tenses
Past Simple

Structure: Subject + past verb form
Use: Describes completed actions in the past.
Examples:
- I visited my grandparents yesterday.
- You saw a movie last night.
- He wrote a letter.
- She cooked dinner.
- It rained last week.
- We played basketball.
- They traveled to London.
Past Continuous

Structure: Subject + was/were + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions that were happening at a specific time in the past.
Examples:
- I was reading when you called.
- You were sleeping at 10 PM.
- He was studying all night.
- She was watching TV.
- It was raining this morning.
- We were eating dinner.
- They were playing football.
Past Perfect

Structure: Subject + had + past participle
Use: Describes actions that were completed before another action in the past.
Examples:
- I had finished my work before dinner.
- You had left by the time I arrived.
- He had eaten breakfast.
- She had seen that movie before.
- It had stopped raining when I woke up.
- We had visited the museum.
- They had traveled to Italy.
Past Perfect Continuous
Structure: Subject + had + been + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions that were ongoing up to a specific point in the past.
Examples:
- I had been studying for two hours before the exam.
- You had been working all day.
- He had been playing the piano for an hour.
- She had been cooking for three hours.
- It had been raining for days.
- We had been traveling for a month.
- They had been building the house for a year.
Future Tenses
Future Simple
Structure: Subject + will + base verb
Use: Describes actions that will happen in the future.
Examples:
- I will call you tomorrow.
- You will visit your friend.
- He will buy a new car.
- She will watch a movie.
- It will rain tomorrow.
- We will travel to Spain.
- They will start a new project.
Check Also:
Difference Between Will & Going to for Future Tense + PDF
Future Tense Exercise Short Stories
Example Sentences in Future Simple Tense with Will
Future Simple Tense Example Sentences & Going to (PDF)
Future Continuous
Structure: Subject + will + be + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions that will be happening at a specific time in the future.
Examples:
- I will be studying at 8 PM.
- You will be working tomorrow.
- He will be playing football.
- She will be cooking dinner.
- It will be raining later.
- We will be traveling next week.
- They will be building a house.
Future Perfect
Structure: Subject + will + have + past participle
Use: Describes actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
Examples:
- I will have finished my homework by 6 PM.
- You will have visited Paris by then.
- He will have bought a new car by next month.
- She will have seen that movie.
- It will have stopped raining by morning.
- We will have traveled to Japan by then.
- They will have started a new job.
Future Perfect Continuous
Structure: Subject + will + have + been + verb + ing
Use: Describes actions that will be ongoing up to a specific point in the future.
Examples:
- I will have been studying for three hours by 9 PM.
- You will have been working for five years by next month.
- He will have been playing the guitar for two hours.
- She will have been cooking for three hours.
- It will have been raining for days.
- We will have been traveling for a month.
- They will have been building the house for a year.
Quick Reference Table
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Subject + base verb | I play tennis. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb + ing | I am studying. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + have/has + past participle | I have finished my homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + have/has + been + verb + ing | I have been reading this book for two hours. |
| Past Simple | Subject + past verb form | I watched a movie yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb + ing | I was reading when she called. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle | I had finished my work before dinner. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had + been + verb + ing | I had been working for three hours before he arrived. |
| Future Simple | Subject + will + base verb | I will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will + be + verb + ing | I will be studying at 8 PM. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will + have + past participle | I will have finished my homework by 6 PM. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will + have + been + verb + ing | I will have been studying for three hours by 9 PM. |
Tips for Mastering Verb Tenses
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice helps solidify your understanding.
- Use Visual Aids: Charts and tables can make it easier to remember structures.
- Make Sentences: Create your own sentences for each tense.
- Watch English Content: Listening to native speakers helps you grasp usage naturally.
- Take Quizzes: Regularly test your knowledge to track your progress.
English Verb Tenses PDF
Download this English Tenses PDF that you can read anywhere.
12 English Tenses Book PDF – download⇓



